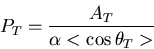![\begin{equation}
\frac{[\sum_{i=1}^{12}N_i(cw)/\sum_{i=1}^{12}N__i(ccw)]_{fwd}}
{[\sum_{i=1}^{12}N_i(cw)/\sum_{i=1}^{12}N_i(ccw)]_{bwd}}\cong 1+4A_{T}.
\end{equation}](eqdoubleratio.png)
In contrast to the previous in-flight-decay experiment,
E246 employs the stopped K+ method.
This technique enables a measurement with coverage of all directions
in the decay phase space including kinematic regions with opposite
PT.
Thus, a double ratio measurement can be carried out with the consequence
of very small systematic errors.
A positive kaon beam with 660 MeV/c is slowed down and stopped
in a target made of 256 scintillating fibers situated in
the center of a superconducting toroidal spectrometer,
which has a large solid angle and wide momentum range with 12 gaps
and analyzes the μ+ momentum.
A TOF system separates μ+ from e+.
The π0 is detected as two photons or one photon
with relatively large energy by a CsI(Tl) calorimeter consisting of
768 crystals.
A K+μ3 decay is identified as coincident
μ+ and π0
which satisfy certain kinematical conditions.
The experimental setup is shown in setup pages.
The momentum analyzed μ+ stops in the polarimeter
and the muon polarization is measured by means of decay positron asymmetry.
If we look at events with pions in the forward(fwd) or
backward(bwd) directions relative to the beam axis,
the direction of PT is either in the clockwise (cw)
or counter-clockwise (ccw) direction in the muon stoppers.
PT is then measured as the asymmetry in cw and
ccw positron emission.
At the Al stopper a magnetic field is applied parallel to azimuthal
PT to preserve it and also to rotate the radial
in-plane polarization components.
The positron asymmetry is then extracted using the following double ratio,
![\begin{equation}
\frac{[\sum_{i=1}^{12}N_i(cw)/\sum_{i=1}^{12}N__i(ccw)]_{fwd}}
{[\sum_{i=1}^{12}N_i(cw)/\sum_{i=1}^{12}N_i(ccw)]_{bwd}}\cong 1+4A_{T}.
\end{equation}](eqdoubleratio.png)